In the manufacturing of large amusement rides, welding craftsmanship is not just an insignificant part of the production process. On the contrary, it forms the foundation of the equipment’s structural safety, durability, and long-term operation costs.
For amusement park ride manufacturers, welding quality represents their technical capabilities and quality control standards. For purchasers and investors, the quality of the welding process directly affects whether the equipment is safe, durable, and worth the long-term investment.
As a manufacturer with over 20 years of experience in the amusement equipment industry, this article will provide a comprehensive guide on:
- The core requirements for welding processes in amusement equipment
- How to control welding quality and avoid common defects
- How welding processes impact equipment safety, costs, and delivery cycles
- How can purchasers professionally assess the welding level of a manufacturer
Let’s help you go from “uncertain about welding” to “able to judge welding quality.”
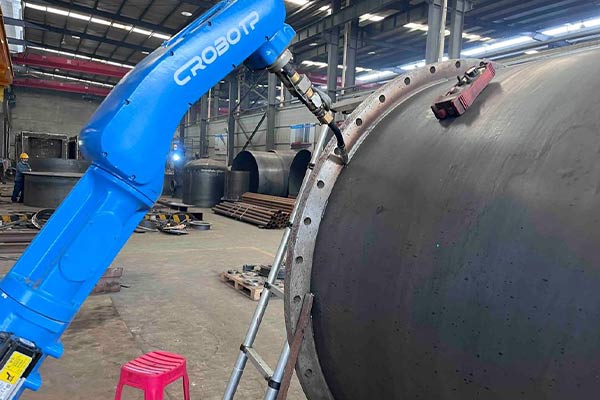
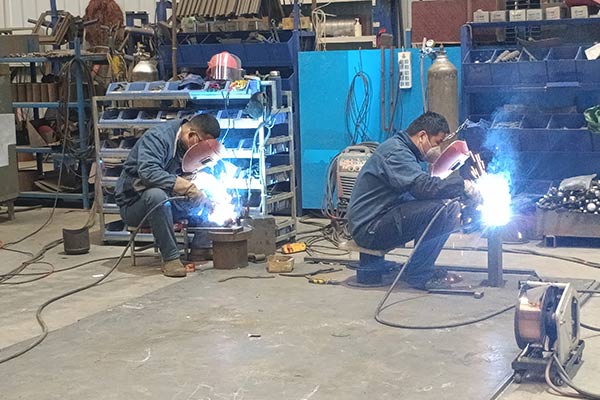


1. Why Is Welding Craftsmanship the Foundation of Amusement Equipment Safety?
Large amusement equipment (such as roller coasters, Ferris wheels, pendulum rides, and drop tower rides) is essentially a complex steel structural system that undergoes:
- Dynamic loads (acceleration, deceleration, shock)
- Cyclic loads (reciprocal motion, rotation)
- Fatigue loads (high-frequency operation)
- Environmental impacts (wind, rain, temperature differences, corrosion)
Welds are not just “connection points”; they are channels for force transfer.
Any issues with critical welds can lead to structural failure, regardless of material quality or design accuracy. Even small welding defects can:
- Cause cracks to propagate
- Decrease structural rigidity
- Compromise safety redundancies
- In extreme cases, this can result in structural instability
Thus, in amusement ride manufacturing, welding craftsmanship must prioritise “structural safety” over efficiency or aesthetics.
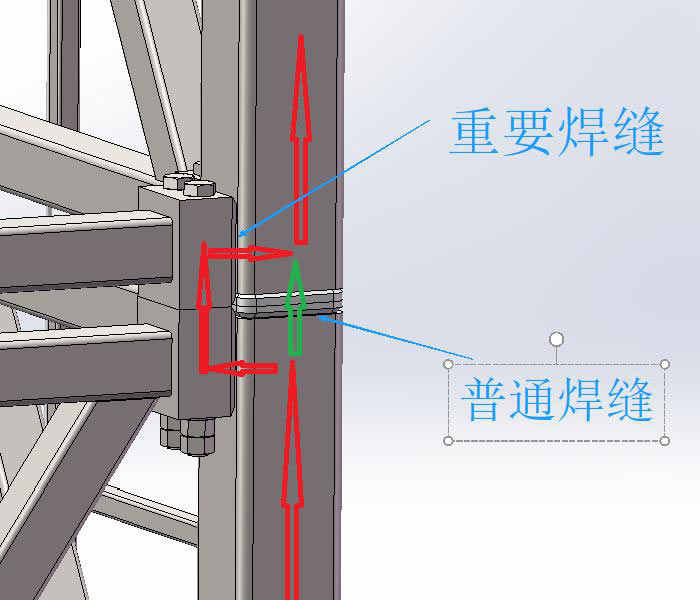
2. Core Requirements for Amusement Equipment Welding Processes
1. Choosing the Right Welding Methods (Dependent on Structure)
Different types of amusement rides and structural components require different welding methods.
Common welding methods and their applications:
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
- Ideal for primary load-bearing structures, thick plate welding
- Stable weld formation, high-quality consistency
- Commonly used for vertical supports, main beams, and rotating components
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) / Metal Active Gas (MAG) Welding
- Suitable for medium-thickness plates and complex geometries
- High efficiency, ideal for mass production
- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding
- Best for precision components, thin plates, or critical joints
- Clean, aesthetically pleasing welds with minimal defects
Mature manufacturers don’t rely on just one welding method but instead use a combination based on structural load and technical requirements.
2. Welding Parameters Control: Current, Voltage, and Heat Input
Welding quality is highly dependent on controlling parameters:
- Welding Current
- Too high → Burnthrough, undercut, coarse-grain structure
- Too low → Incomplete fusion, slag inclusion, weak joints
- Arc Voltage
- Affects weld width and formation
- Hand arc welding is typically controlled at 20V–25V to avoid excessive arc length or excessive voltage
- Heat Input Control
- Excessive heat → Cracking, distortion
- Insufficient heat → Incomplete welds, reduced fatigue performance
Professional manufacturers strictly control welding parameters through:
- Welding procedure qualifications (WPS)
- Pre-heating and post-weld cooling
- Symmetrical welding sequences to control heat input
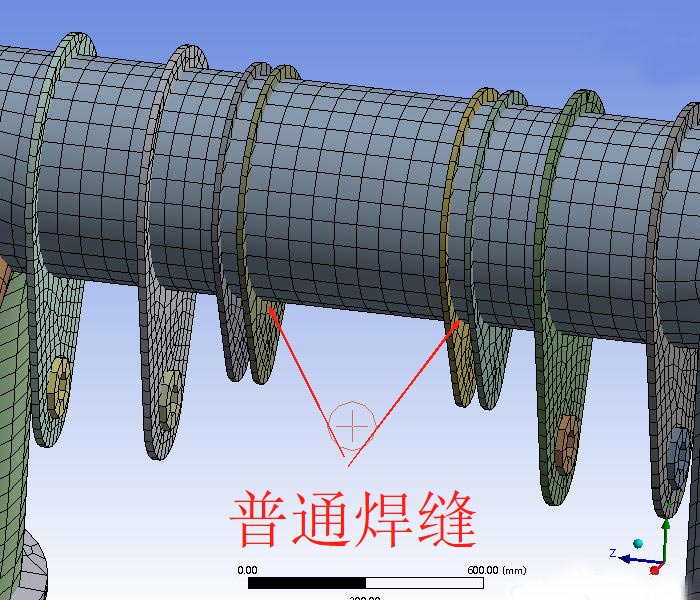
3. Welding Quality Control: How to Avoid Common Welding Defects?
Common Welding Defects and Risks
| Welding Defect | Potential Risks |
| Cracks | Easily propagate, directly threaten structural safety |
| Porosity | Reduces weld strength and fatigue life |
| Slag Inclusion | Creates stress concentration points |
| Incomplete Fusion | Reduces actual load-bearing capacity |
Quality Control System for Welding
To avoid defects, we implement a comprehensive quality control system:
- Pre-welding Control
- Checking groove dimensions and assembly gaps
- Confirming correct weld preparation and positioning
- Welding In-Process Control
- Qualified welders’ skill management
- Real-time monitoring of welding parameters
- Post-Welding Inspection
- Visual inspection (shape and dimension)
- Non-destructive testing (UT / MT / RT)
- Documentation and traceability of key welds
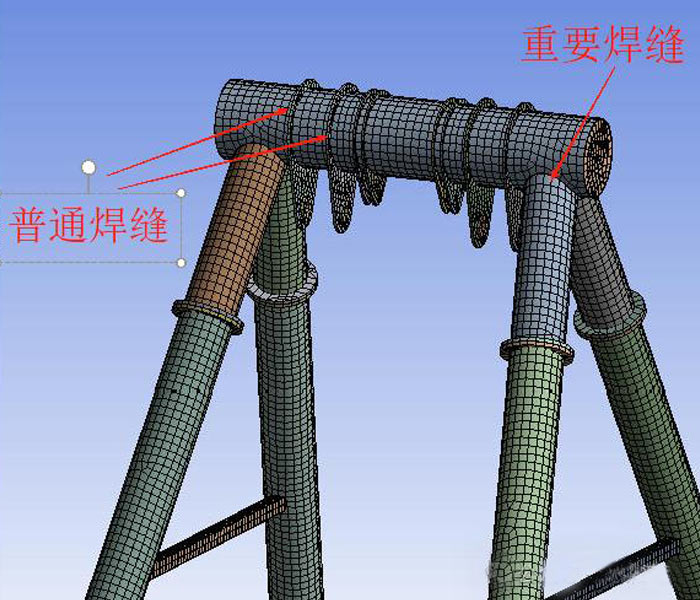
4. How Welding Affects Equipment Quality, Cost, and Delivery Time
1. Impact on Equipment Quality
- Welding quality = structural safety baseline
- Determines equipment fatigue resistance and lifespan
- Directly affects inspection and certification compliance
2. Impact on Production Costs
Optimised welding processes do not necessarily increase costs; they can lower costs in the following ways:
- Reducing rework and material waste
- Lowering maintenance frequency
- Minimising downtime due to welding failures
3. Impact on Production Cycles
- Standardised welding processes → manageable production
- Automated/robotic welding → increased efficiency
- Mature processes → stable delivery timelines
5. How Can Purchasers Assess a Manufacturer’s Welding Process Quality?
This is often the most overlooked but the most valuable part of the procurement process.
1. Look at the “Documents,” Not Just the Samples
Key documents to request from manufacturers include:
- Welding procedure qualifications (WPS / PQR)
- Certifications for compliance with standards like ISO 3834 or EN 1090
- Complete welding inspection reports
2. Look at the “Logic,” Not Just the Promises
Ask the manufacturer:
- How do you distinguish between critical and non-critical welds?
- What is your process for testing critical welds?
- How do you manage welder qualifications?
- Do you use different welding processes for different amusement park equipment?
Clear and professional answers are a strong indicator of a trustworthy amusement equipment manufacturer.
3. Look at the “Long-Term Thinking”
Mature manufacturers focus on:
“Will this amusement rides be safe and durable after 10, 15, or 20 years?”
Instead of only focusing on the initial production.
Conclusion: Welding Craftsmanship Defines the Safety Baseline for Amusement Equipment
The safety of large amusement equipment is never determined by a single component; it is the result of a combination of design, materials, and manufacturing processes.
Among these, welding craftsmanship is the most fundamental but often underestimated element.
At Carnee Rides, with over 20+ years of manufacturing amusement park ride experience, Carnee Rides maintains the philosophy that:
Welds are not just cost points; they are safety points.
Only by perfecting welding processes can amusement equipment truly be safe, durable, and capable of sustained operation.
If you would like to learn more about our amusement ride manufacturing processes, quality standards, or theme park project solutions, feel free to reach out for an in-depth discussion.










